User data collection and identity verification have become significant features in various industries. Data has become vital in making critical e-commerce, healthcare, finance, and social media decisions in today’s digital age.
Despite the apparent benefits of user data collection and identity verification, ignoring the ethical concerns they raise is impossible.
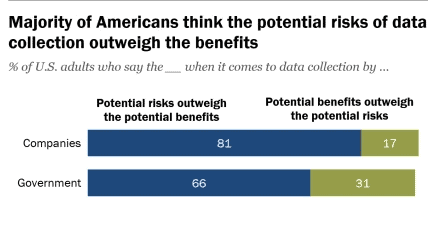
Users must remain confident about privacy, consent, and discrimination. Recent studies by the Pew Research Center show about 81% of Americans believe the risks of sharing their data outweigh the benefits.
Therefore, organizations must seriously consider the ethical implications of their user data collection and identity verification procedures. This way, they ensure they remain honest, open, and respectful of their users’ rights.
This article will examine vital ethical considerations in user data collection and identity verification. We will also reveal practical measures to help organizations humanely and legitimately handle these considerations.
Consent Management

Consent management refers to the means stakeholders use to obtain users’ explicit permission before collecting, storing, sharing, and using their data.
Imagine being asked by a salesperson at the store for your email address. He tells you the store will send regular promotional offers to your email address. If you provide your email address, then you have given consent.
But if you begin receiving promotional offers from the store after they collect your email address without asking you first, they have violated your privacy. This breach of trust is illegal and punishable by relevant authorities.
According to Priyam Chawla, Marketing Manager at Jolly SEO, “Consent management also requires stakeholders to remain honest about what data they are collecting and how it will be handled. Users must never be fearful for their safety or privacy at any time. Organizations must reassure users by providing clear privacy policies that users can study before consent.”
Social media platforms also significantly affect user data collection and consent management. Think about how social media networks request access to your contacts, location, and personal data.
They rely on user consent to provide targeted advertising, personalized recommendations, and social connections. However, users must be aware of the information they share and its potential implications.
By understanding the consent management processes within social media platforms, users can make informed choices and take control of their digital footprint.
Finally, consent management involves regular audits of data usage to prevent misuse and unauthorized access. This way, sensitive data such as medical records and financial information never get into the wrong hands.
Data Security and Confidentiality

Data collection from users has progressively grown in significance for companies as it aids them in comprehending consumer behavior and preferences. This knowledge empowers them to devise efficient tactics to optimize their profits and track the right product marketing metrics.
Nonetheless, user data typically encompasses lots of personal and delicate data.
For instance, suppose you manage a web development agency, your customers might depend on you to create and maintain websites that manage user information. To secure the confidence of your customers, you need to assure the protection and privacy of the data you gather and store.
Encryption plays a vital part in ensuring the security and confidentiality of user data and identity. It covers the process of encoding user information, rendering it incomprehensible to anyone lacking the appropriate key. Consequently, it aids in safeguarding consumers’ data even in the event of a data breach.
Access control lists (ACLs) are another vital data security and confidentiality aspect. They further streamline data accessibility by authorized personnel. ACLs ensure that only personnel with legitimate needs can view or modify sensitive data.
To illustrate, a healthcare organization may implement strict ACLs for patient records, granting access only to healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care. By limiting access to authorized personnel, the organization maintains the confidentiality of sensitive medical information and prevents potential breaches.
It is essential that organizations embrace rigorous security protocols, including the use of a Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) tool when storing any information they gather. They have the option to employ firewalls and secured servers to offer adequate defense against breaches and alternative types of cyber-attacks.
In today’s interconnected world, where social media platforms play a significant role in user engagement, it’s crucial to address the impact of social media on data security. Organizations must be aware of the risks associated with social media data collection and take appropriate measures to protect user privacy.
For instance, consider a social media marketing agency that collects user data through social media channels. They should ensure compliance with platform policies and regulations, obtain explicit user consent for data collection, and employ robust security measures to safeguard the information they gather.
Organizations should also review and guarantee the implementation of data security best practices. In doing so, they can sustain a sense of assurance that user data remains shielded against the most recent bugs and cyber-attacks.
Additionally, stakeholders must consider data minimization. This principle requires organizations to gather only the data relevant to their needs and nothing more. Data minimization helps to eliminate the leak or misuse of sensitive data.
Fairness and Equity

Fairness and equity are essential to establishing a functioning digital ecosystem. Fairness embodies the principle of treating every party involved equally and overlooking any form of bias.
Consider a scenario where a social media platform collects user data for targeted advertising. Fairness dictates that the platform collects the same data from all users, regardless of their backgrounds, preferences, or demographics. This approach ensures that no particular group is disadvantaged or targeted unfairly based on their characteristics.
Equity means creating a level playing field for every user by considering any limitations people may have during user data collection and identity verification. It also involves providing unique support users might require to access specific opportunities.
These considerations require stakeholders to collect the same data from every user in any population. They also ensure that stakeholders consistently manage and use user data reports.
This way, organizations avoid discriminating against certain groups or putting them at a disadvantage when using their data.
Also, fairness and equity ensure that every user gets an equal opportunity to verify their identity without being discriminated against.
Stakeholders might need to provide alternative verification methods for users who may be physically impaired or unable to access conventional means of identification for any reason.
Transparency

Transparency is the bedrock of trust and remains one of the most vital user data collection and identity verification concepts.
Imagine you’re signing up for a new service or making a purchase online. As a user, you deserve to know how your data is handled. Transparency ensures that organizations are upfront about their data collection practices, who has access to your information, and how it is used.
It involves openly, honestly, and ethically handling user data collection and identity verification. Transparency also requires honesty about who has access to user data and how user data is used.
Transparency also gives users more control over their data. Users deserve to know how their data is handled.
Without transparently collecting user data, stakeholders breed suspicion and mistrust amongst users. Lack of transparency leads to user privacy violations, which could harm individuals and specific groups.
Organizations can ensure transparency by providing clear privacy policies showing how user data is gathered, stored, and utilized.
Users must be able to understand the terms of any privacy policy and easily access it whenever they wish.
Privacy policies must also be periodically updated to reflect changes in handling and managing user data collection and identity verification. Implementing Identity security posture management further reinforces transparency efforts by systematically assessing and managing the security measures surrounding user identity data, ensuring compliance with privacy policies and regulatory standards, and fostering trust between users and organizations.
Transparency becomes even more critical in the social media landscape due to the potential misuse of user data.
Social media platforms play a significant role in user data collection and identity verification. They gather vast information through user profiles, interactions, and content.
Recent scandals involving social media platforms have highlighted the importance of being transparent with users about how their data is handled and protected.
Data Governance

Data administration encompasses the protocols and directives surrounding user information compilation and identity authentication.
This moral deliberation necessitates that establishments entirely adhere to applicable statutes in managing and employing user information.
It guarantees openness and thwarts privacy infringements. It also averts the mishandling or dissemination of user information to unapproved third parties.
Thus, data governance safeguards users and certifies that they stay well-informed about handling their data.
This ethical consideration also requires that organizations allow only authorized personnel to process data. This way, data governance prevents the indiscriminate sharing of data and minimizes the risk of data leaks.
In the context of social media, data governance also involves carefully managing data sharing on a need-to-know basis. Only stakeholders with legitimate reasons and appropriate permissions can access user data.
By strictly controlling access, the platform minimizes the risk of data misuse or unauthorized access, bolstering user trust and safeguarding their privacy.
Data governance also requires stakeholders to comply with the relevant legislation when storing data. This way, data is stored only on secure channels for as long as necessary. Examples of such legislation include the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe.
Lastly, data governance provides adequate guidelines for the disposal of user data. It ensures that data is erased and impossible to recover.
Accuracy and Accountability

Accuracy describes the correctness of any data that is gathered and verified. Put simply, data must be truthful and represent existing realities correctly.
Accuracy is essential because incorrect data can result in the creation of unhelpful policies. Besides resulting in the mismanagement of public resources, inaccurate data could also harm society members.
Imagine a government agency that assumes that most of its target population is older than they are based on inaccurate data. This agency may spend more of its budget on less essential projects and run into problems in the long run.
Accountability describes the responsibility of stakeholders to handle the data they collect ethically. They must remain transparent about how they gather and use data.
It is also essential to keep data secure and not use it in ways that could hurt individuals or specific groups.
Consider an organization that collects data based on people’s political preferences through social media platforms. To maintain accountability, this organization must take appropriate measures to ensure that the data they collect is not used to discriminate against individuals or manipulate public opinion.
With their vast user bases and extensive data collection capabilities, social media platforms present unique challenges in terms of accuracy and accountability.
Companies operating in this space must be diligent in verifying the authenticity and reliability of the data they collect from users. They should also have robust mechanisms in place to safeguard user privacy and prevent the misuse of personal information.
One notable example is the Cambridge Analytica scandal, where a political consulting firm misused Facebook user data to target individuals with tailored political content without their explicit consent. This incident shed light on the importance of strict data handling practices and the need for accountability in the social media realm.
Final Thoughts on User Data Collection
Ethical considerations in user data collection and identification are crucial to establishing a functional and sustainable digital ecosystem.
Creating a framework that protects user privacy and ensures user security is vital as we spend more time online and live on several digital platforms.
Effective, ethical practices ensure that stakeholders remain transparent in their handling of user data and respectful of user rights.
This way, they establish functional consent management processes, audit data usage periodically, and implement only secure and ethical identity verification.
Finally, as individuals, we also play a crucial role in promoting ethical practices. We must demand more transparency from relevant organizations and keep up with evolving trends in data management and user protection.
